TM 5-3895-359-14&P
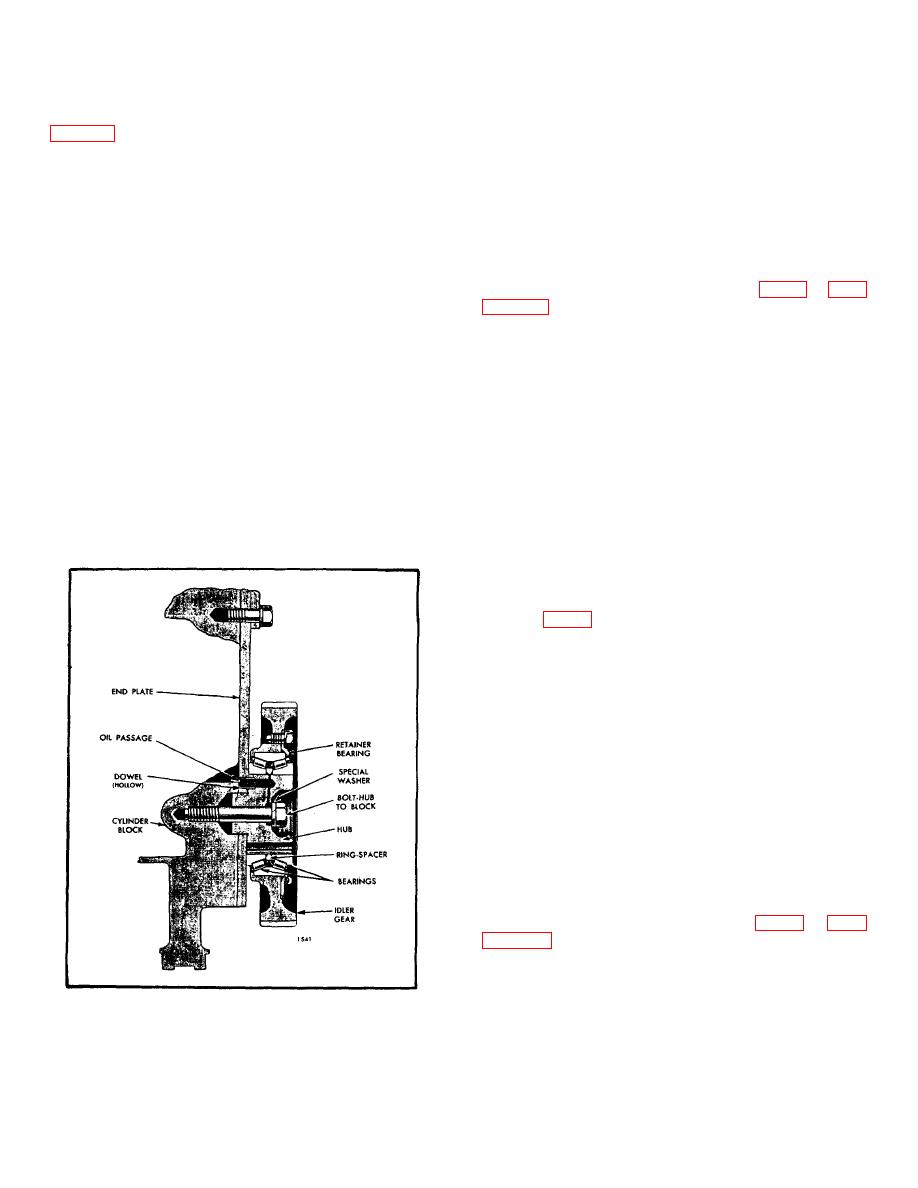
IDLER GEAR AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
spacer was used on early design bearings. The bearing
type idler gear. The early flanged type idler gear and
cup(s) has a light press fit in the idler gear and is held
the former single spacer type idler gear are no longer
against a flanged lip inside the idler gear on one side
serviced.
When replacing any part of the gear
and by a bearing retainer secured with six bolts and
assembly a complete current roller bearing type idler
three bolt locks on the other side.
gear assembly must be used.
A right-hand helix gear is provided for left-hand rotation
The idler gear is mounted on a double row, tapered
engines, and a left-hand helix gear is provided for right-
roller bearing which, in turn, is supported on a stationary
hand rotation engines. Since the engine is right hand
hub. This hub is secured directly to the cylinder block
by a bolt which passes through the hub and rear end
plate. A hollow dowel serves a two-fold purpose; first,
as a locating dowel it positions the hub and prevents it
An idler gear hole spacer (dummy hub) is used on the
from rotating and, second, conducts oil under pressure
side opposite the idler gear. NO gasket is used between
from an oil gallery in the cylinder block through a
the idler gear hub or dummy hub and the flywheel
passage in the gear hub to the roller bearing.
housing. The flywheel housing bears against the inner
races of the idler gear bearing and also against the
The current idler gear bearing consists of two cups, two
dummy hub. Three self-locking bolts and steel washers
cones and an outer and inner spacer ring. The former
are used to attach the flywheel housing at the idler gear
idler gear bearing consists of a cup, two cones and a
and dummy hub locations. The washers seat in 7/8"
spacer ring.
spot faces at the flywheel housing attaching bolt holes,
thus preventing oil leakage at these locations.
The inner and outer cones of the idler gear bearing are
pressed onto the gear hub and, therefore, do not rotate.
Remove Idler Gear, Hub and Bearing Assembly and
Spacer rings or a spacer, separate the cones. No
Idler Gear Hole Spacer (Flywheel Housing
Previously Removed)
1. Remove the idler gear hub to cylinder block bolt and
washer (Fig. 1) and withdraw the assembly from the
cylinder block rear end plate.
NOTE:
Before removing the idler gear check
the idler gear, hub and bearing
assembly for any perceptible wobble
or shake when pressure is applied;
by firmly grasping the rim of the gear
with both hands and rocking in
relation to the bearing. The bearing
must be replaced if the gear wobbles
or shakes. If the gear assembly is
satisfactory, it is only necessary to
check
the
pre-load
before
reinstallation,
completely reconditioned.
Disassemble Idler Gear, Hub and Bearing Assembly
Fig. 1. Idler Gear Mounting Typical
While removing or installing an idler gear bearing, the
bearing MUST be rotated to avoid the possibility of
damaging the bearing by brinelling the bearing cones.
Brinelling refers to the marking of the cones by applying
a heavy load through the rollers of a non-
10-2-117


