TM 5-3895-359-14&P
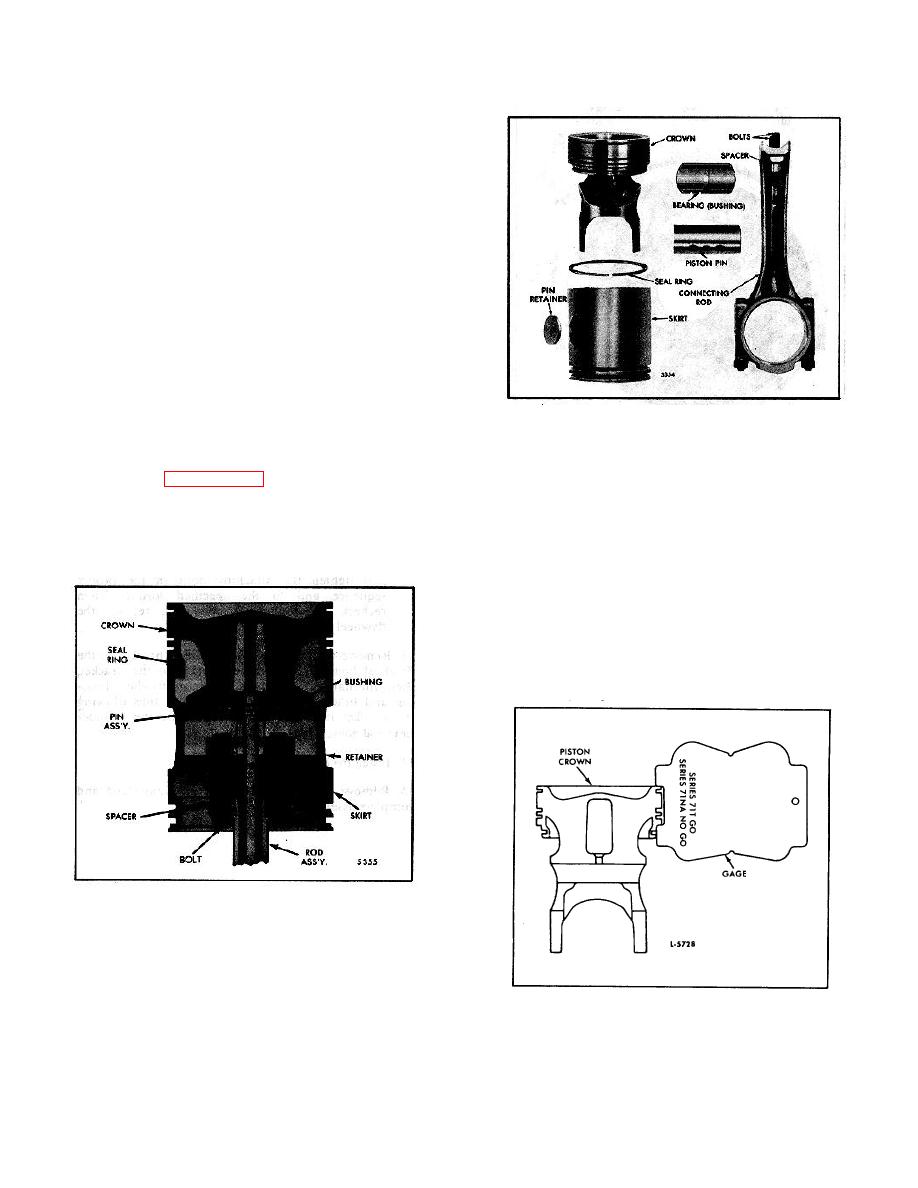
CROSS-HEAD TYPE PISTON
The cross-head piston (Figs. I and 2) is a two-piece
piston consisting of a crown and skirt. A metal oil seal
ring is used between the crown and skirt which are held
together by the piston pin. Ring grooves are machined
in the piston crown for a fire ring and two compression
rings. The crown is also machined to accept a
150 lipper type bushing (bearing). The piston skirt
s
incorporates two oil control ring grooves, piston pin
holes and piston pin retainer counterbores. Equally
spaced drain holes are located in the oil ring groove
area to permit excess oil, scraped from the cylinder
walls, to return to the crankcase. A lubricating oil tube
and floating nut are contained inside of the piston pin.
Two bolts and spacers are used to attach the connecting
rod to the floating nut in the piston pin.
Detroit Diesel engines are designed to operate on diesel
fuels containing less than 0.5% sulfur. Plasma-faced
fire rings may be used in areas where approved fuel is
Fig. 2. Cross-Head Piston and Connecting Rod
not commercially available or economically feasible to
Components
obtain. It should be recognized that even with the use of
Internal parts of the piston are lubricated and cooled by
the high sulfur fuel modification and maintenance
the engine lubricating oil. Oil is pressure-fed up the
procedures (see Page 10-9-7), engine life may still not
drilled passage in the connecting rod. through the oil
equal that with our recommended fuels.
tube in the piston pin. then through the center hole in
NOTE
the bushing to the underside of the piston crown. A
Recommended engine modifications
portion of the oil flows along the grooves in the bushing
do not apply to U.S.
certified
to lubricate the piston pin.
automotive engines.
During engine operation, gas loads pushing down on the
piston crown are taken directly by the piston pin and
bushing. The piston skirt, being separate, is free from
vertical load distortion; thermal distortion is also reduced
as the piston crown expands. As the connecting rod
swings to one side during downward travel of the piston,
the major portion of the side load is taken by the piston
skirt.
Fig. 1. Cross-Head Piston and Connecting Rod
Assembly
Fig. 3. Piston Identification using Gage J 25397
10-2-78


