TM 5-3895-359-14&P
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
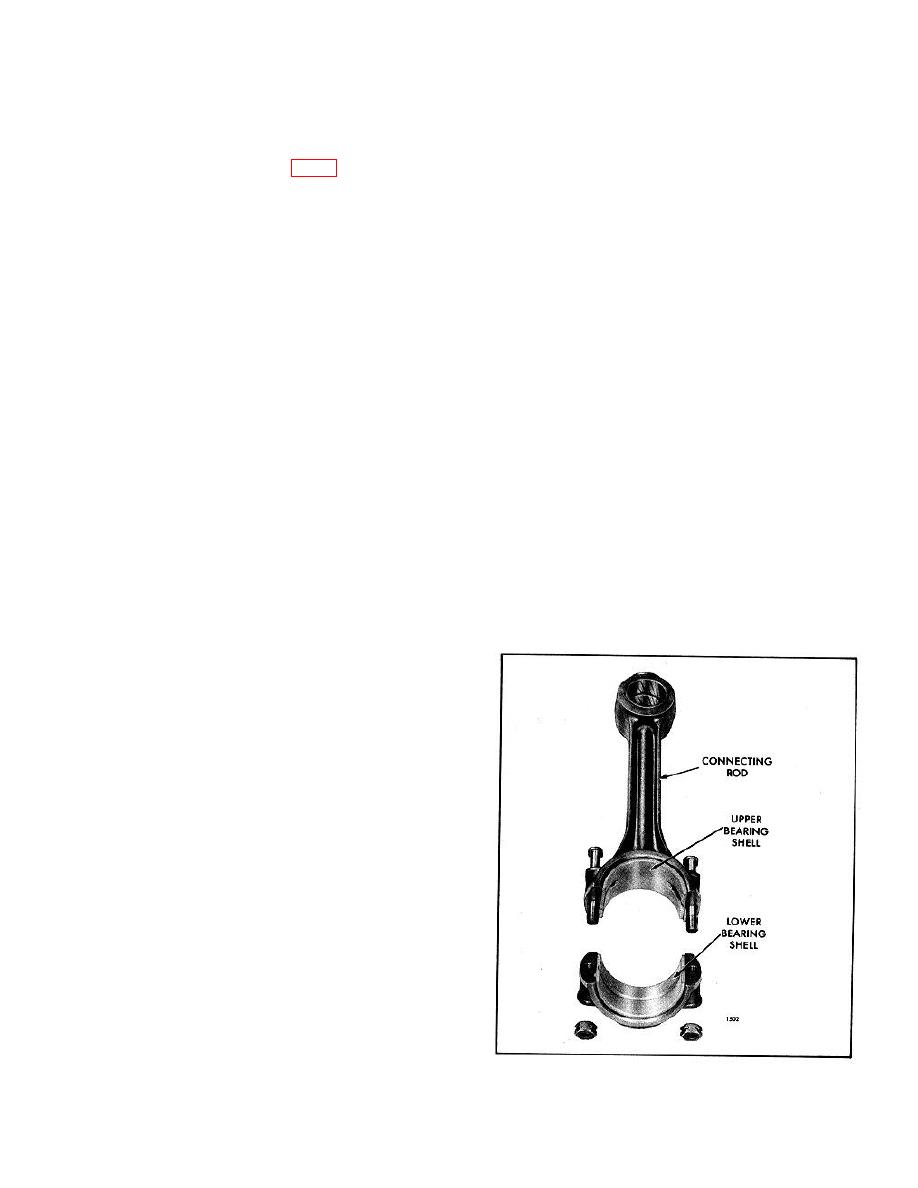
The connecting rod bearing shells (Fig. 1) are precision
NOTE: If shims are used between the oil pump
made and are replaceable without shim adjustments.
body and the main bearing caps, save the shims
They consist of an upper bearing shell seated in the
so they may be reinstalled when installing the oil
connecting rod and a lower bearing shell seated in the
pump.
connecting rod cap. The bearing shells are prevented
from endwise or radial movement by a tang at the
parting line at one end of each bearing shell.
3. Remove one connecting rod bearing cap. Push the
piston and rod assembly up into the cylinder liner far
Various types of bearings have been used. Currently,
enough to permit removal of the upper bearing shell.
multiple layer copper-lead coplated or aluminum
Do not pound on the edge of the bearing shell with a
triplated bearings are in use. These bearings have an
sharp tool.
inner surface, called the matrix, of copper-lead or
aluminum. A thin deposit of babbitt is then plated onto
4. Inspect the upper and lower bearing shells as
the matrix. This babbitt overlay has excellent resistance
outlined under Inspection.
to friction, corrosion and scoring tendencies which,
combined with the material of the matrix, provides
5. Install the bearing shells and bearing cap before
improved load carrying characteristics. These bearings
another connecting rod bearing cap is removed.
are identified by the satin silver sheen of the babbitt
when new and a dull gray after being in service. The
former copper-lead bearings had a copper color when
Inspection
new and turned very dark during engine operation.
Bearing failures may result from deterioration (acid
The upper and lower connecting rod bearing shells are
formation) or contamination of the oil or loss of oil. An
different and are not interchangeable.
The upper
analysis of the lubricating oil may be required to
bearing shell is grooved midway between the bearing
determine if corrosive acid and sulphur are present
edges, part way up from each parting line, with an oil
which cause acid etching, flaking and pitting. Bearing
hole through the shell at the termination of each groove.
seizure may be due to low oil or no oil.
The lower bearing shell has a continuous oil groove,
extending from one parting line to the other, in line with
that of the upper bearing shell. These grooves maintain
a continuous registry with the oil hole in the crankshaft
connecting rod journal, thereby providing a constant
supply of lubricating oil to the connecting rod bearings,
piston pin bushings and spray nozzle through the oil
passage in the connecting rod.
Remove Bearing Shells
The connecting rod bearing caps are numbered 1, 2, 3,
etc., with matching numbers stamped on the connecting
rods. When removed, each bearing cap and the bearing
shells must always be reinstalled on the original
connecting rod.
Remove the connecting rod bearings as follows:
1. Drain the oil and remove the oil pan.
2. Remove the lubricating oil pump and the pump inlet
and outlet pipes.
Fig. 1 - Connecting Rod and Bearing Shells
10-2-90


