TM 5-3895-359-14&P
extending into the journal fillet. If main bearings are
circumferential fillet cracks at the critical areas and 45
replaced due to one or more badly damaged bearings, a
cracks (45 with the axis of the shaft) starting from
careful inspection must be made to determine if any
either the critical fillet locations or the connecting rod
cracks have started in the crankshaft. These cracks are
journal holes as shown in Fig. 5. Replace the
most likely to occur on either side of the damaged
crankshaft when cracks of this nature are found.
bearing.
Crankshaft Grinding
Torsional fatigue failures result from torsional vibration
which takes place at high frequency.
In addition to the standard size main and connecting rod
bearings, .002 ", .010", .020" and .030" undersize
A combination of abnormal speed and load conditions
bearings are available.
may cause the twisting forces to set up a vibration,
referred to as torsional vibration, which imposes high
NOTE:
stresses at the locations shown in Fig. 4.
The .002 " undersize bearings are
used only to compensate for slight
Torsional stresses may produce a fracture in either the
wear on crankshafts on which
connecting rod journal or the crank cheek. Connecting
regrinding is unnecessary.
rod journal failures are usually at the fillet at 45 to the
axis of the shaft.
If the crankshaft is to be reground, proceed as follows:
A loose, damaged or defective vibration damper, a
1. Compare the crankshaft journal measurements taken
loose flywheel or the introduction of improper or
during inspection with the dimensions in Table 2 and
type of failure. Also, overspeeding of the engine or
to be reground.
resetting the governor at a different speed than intended
Conn. Rod
Main Bearing
for the engine application may be contributory factors.
Bearing
Journal Dia.
Journal Dia.
Sizes
A
"B
As previously mentioned, most of the indications found
Standard
2.750"
3.500"
during inspection of the crankshaft are harmless. The
.002" Undersize
2.750"
3.500"
two types of indications to look for are
.010" Undersize
2.740"
3.490"
.020" Undersize
2.730"
3.480"
.030" Undersize
2.720"
3.470"
TABLE 2
2. If one or more main connecting rod journals require
grinding, then grind all of the main journals or all of the
connecting rod journals to the same required size.
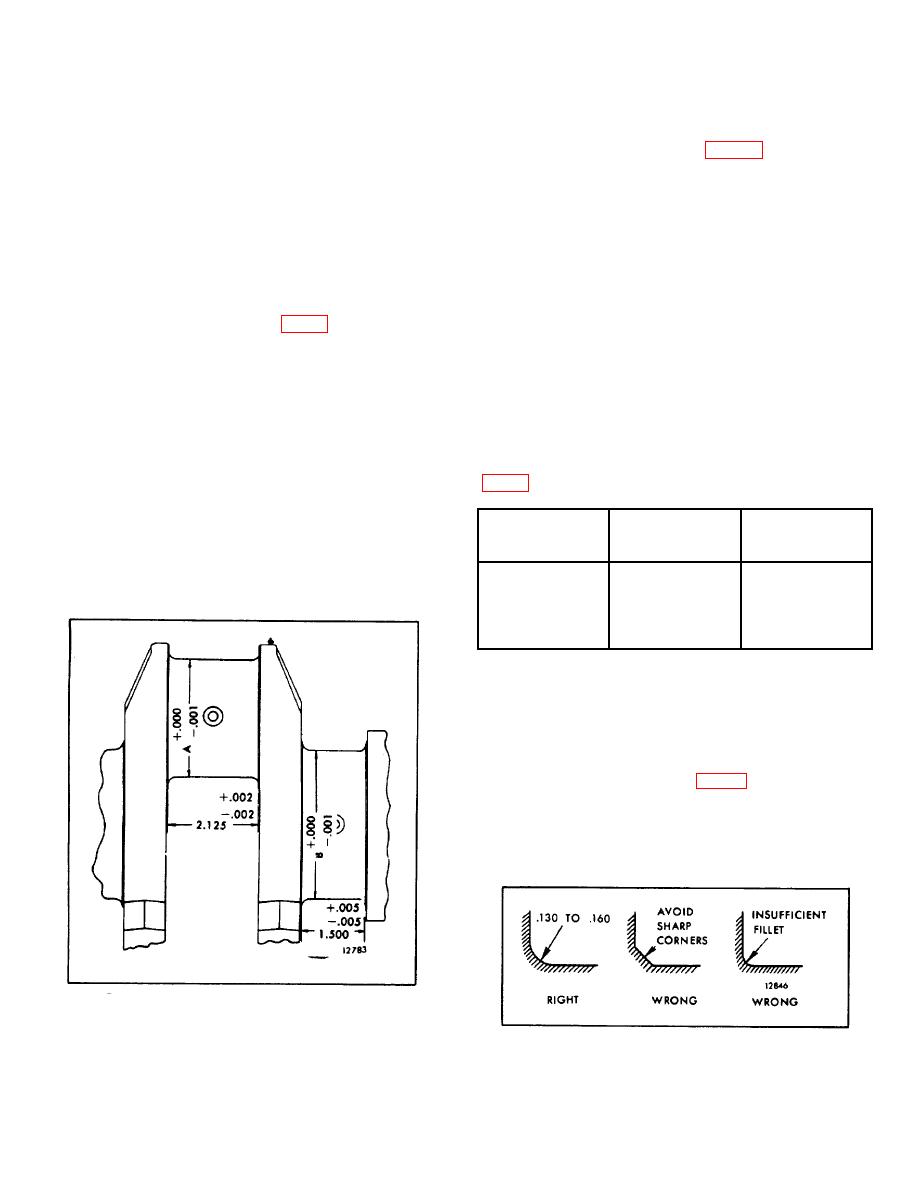
3. All journal fillets must have a .130 " to .160 " radius
between the crank cheek and the journal and must not
have any sharp grind marks (Fig. 7). The fillet must
blend smoothly into the journal and the crank cheek and
must be free of scratches. The radius may be checked
with a fillet gage.
4. Care must be taken to avoid localized heating which
Fig. 6. Dimensions of Crankshaft Journals
Fig. 7. Crankshaft Journal Fillets.
10-2-52


